SEO fundamentals #
What is SEO? #
Search engine optimisation (SEO) is the process of growing a website’s organic search traffic. It’s where you do things that help you show up and rank higher in a search engine’s organic results (predominantly Google, can also be followed across to Bing and international search engines).
Why is SEO important? #
People are likely searching for what we do (kids holiday camps, toddler football classes, wraparound care in schools), and you can attract customers by ranking for those terms. But you’re unlikely to rank without effort, as others are trying to do the same. This is why SEO matters. It helps show Google that you most deserve to rank.
What are the benefits of SEO? #
Most people click one of the first few search results, so higher rankings usually lead to more traffic. Unlike other channels, search traffic tends to be consistent and passive. That’s because the number of searches is usually quite consistent month to month.
SEO is essentially the FREE version of paid advertising (which will jump you to a more recognised position on google – with a cost allocated to this).
How can Network Partners help? #
Blog Posts #
Blogging keeps your website fresh and current #
Google doesn’t want to deliver its searchers outdated information. Websites that are regularly updated signal to them that the website is alive and offering fresh content. It also gives the search engine algorithms more reason to index your website more often, keeping it more on their radar over time.
It’s not a good business move (and sometimes impossible!) to update pages such as the Homepage or venue pages – so a blog is a more practical tool for adding new content to your website on a regular basis.
Blogs can improve users time on page. #
Google’s number one priority is providing the people performing searches with the information they’re looking for, so they’ll keep coming back to use Google again. If someone who does a search clicks on the first link, then finds it unhelpful and immediately leaves to go back to the search page – that tells Google that the first result wasn’t as helpful as they thought. On the other hand, when someone clicks on a result and stays on the website for a while, that signals to Google that this website is actually very helpful.
Someone who comes to your website from a blog post that shows up in the search results is going to have more reason to stick around for a while and read the whole thing than someone who lands on a page with less text or information.
Blogging helps you target SEO optimised long-tail keywords #
A lot of people start out doing SEO wanting to aim for the most relevant keywords for your business. For example, at Sport4Kids, we will be targeting keywords such as “Toddler Football Classes” or “Kids Holiday Camps”
SEO is really competitive, and we are constantly competing with companies like Diddikicks/Rugby Tots who will have a website solely built towards one service line – therefore the best bet for most brands in a competitive space is to look for longer, more specific keywords people are searching for that are relevant to the business and try to rank for those.
These are called long-tail keywords and they’re extremely important for any SEO strategy – half of all searches are for terms that are four words or longer. But they can be awkward to try to fit into your product pages. However, they’re the perfect kind of terms to target in a blog post. An example would be a blog on “Fancy Dress Ideas for Children’s Halloween” or “Top 10 Benefits for Children to start Sports at a Young Age” – these individuals searching for these terms are likely parents with a vested interest in their children’s needs/wants.
These searches don’t attract as much traffic as “Toddler Fooball Classes” does, but they come from people clearly in your target audience of parents and, if you can make it onto page one, you’ll get way more traffic from these topics than you would on page five or ten for broader more popular terms.
A blog gives you opportunities for internal linking. #
So much of SEO is about links and internal links are the easiest ones for you to get since you can create them for yourself. Failing to include internal links on your website that point users from one page on the site to another is one of the simplest SEO mistakes you can make.
While you can probably find some good internal linking possibilities on the main pages of your website, once you start publishing blog posts, the opportunities will really blossom. As you add more pages on various but related topics, you add more opportunities to naturally link those pages to each other.
Every time you do so, you can strategically use the anchor text to better tell Google what the page you’re linking to is about – strengthening its connection to your target keywords in how the algorithm sees it.
A blog helps you connect with your audience. #
This isn’t a direct linking factor like links are, but it is something that significantly contributes to linking factors. When your audience reads a post they love, they’re more likely to share it, drive more traffic to it, come back to your website again to see more of your content and maybe even sign up for your email list. When you get lots of traffic and repeat visitors, that shows Google that people like your website and raises your authority level in their algorithm.
Best Practice with Imagery on the Website #
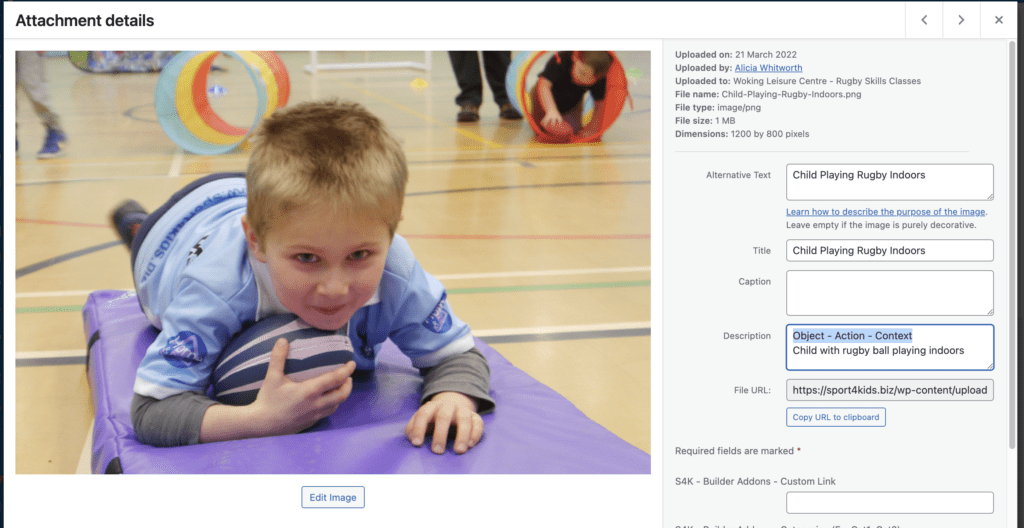
Use relevant, accurate alt text for user accessibility and SEO. #
Alt text is written copy that describes an image. For instance, if you click on Sport4Kids Homepage Image you will see it is named correctly as “Child playing with rugby ball indoors”
This can be set in the “Media Library” in the back-end of the website.
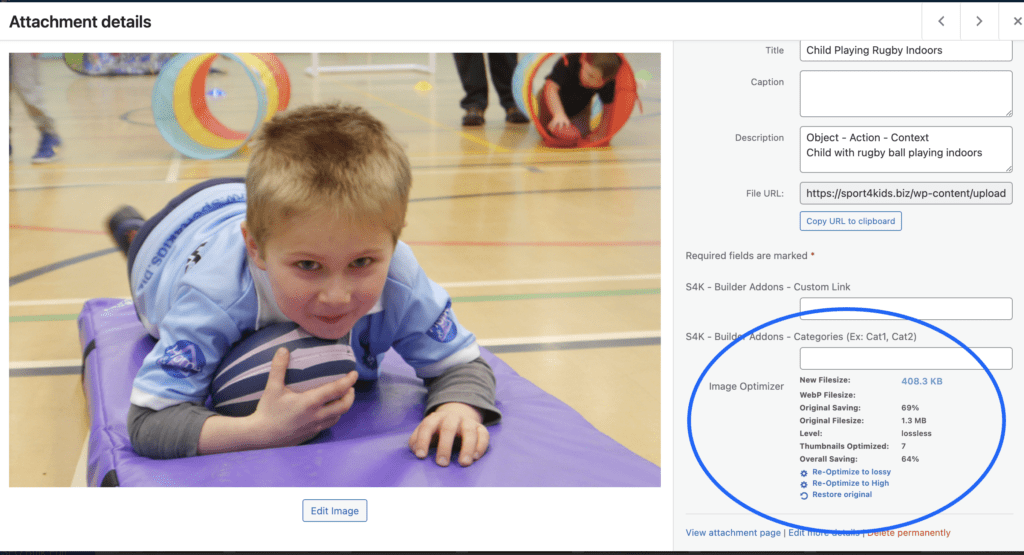
Compress images for faster load time. #
Compressing images is a vital component of any good website optimisation strategy. It helps pages load faster, provides a better user experience and also helps boost SEO rankings!
Typically, less than 100 KB is ideal in terms of good file size. The WordPress site provides an option for this in the “Media Library” – see attached.
However, it’s important to note — Google doesn’t look at each individual image size. Instead, it looks at total page size.
So, if you have a small image where quality differences are less substantial, then you might try compressing that image to 30-50 KB … which gives you extra room to keep another image 30 KB bigger, particularly if that image loses quality after compression.
Post original images — not just stock photos. #
Ultimately, Google (and readers) prioritise original content — which should be easy enough for our business and having such a hands-on approach with our product.
If your image doesn’t accurately demonstrate your product, it will get buried under better, higher-quality images from competitors- so it is important to have relevant images, with a modern approach.
Canva graphics will also count as unique and original content!
Name your file images before uploading them. #
Your file name can impact how easy it is for search engine crawlers to interpret your image, so it’s helpful to rename your file before uploading it onto your webpage.
Rather than keeping the name a generic “IMG_0883”, try using relevant keywords to describe what’s in the image, similar to your alt text. This can also help ensure your image appears on the image search results page, which will increase traffic to your site.
Title Tags/Descriptions #
What are title tags and meta descriptions? #
Title tags and meta descriptions are bits of HTML code in the header of a web page. They help search engines understand the content on a page. A page’s title tag and meta description are usually shown whenever that page appears in search engine results.
Well written and compelling meta tags can attract more users to click to your website from the search engine results.
The title tag #
The title tag is the title element of a web page that summarises the content found on a page. It will appear in three key places: browsers, search engine results pages, and external sites such as Facebook or Twitter. We’ll look at examples of title tags later.
There’s one important thing to keep in mind. Search engines expect a titles tag to include relevant keywords and phrases that describe what that page is about. So if the title you create is not relevant for the page, Google can choose to show a different title instead. You don’t want that to happen. Why? Because title tags are a great opportunity to attract prospects to click through to your site so make sure it gives an accurate, concise and compelling summary of what that page is about.
The meta description #
The description tag is intended to be a short summary of the content found on the web page. While the title tag is very limited, a meta description gives you a bit more space to tell users what you’re offering, and it’s an opportunity to give them a compelling reason to click through to your page.

 Cricket Classes
Cricket Classes Dance Classes
Dance Classes Family Events
Family Events Football Academy
Football Academy Football Classes
Football Classes Football Tournaments
Football Tournaments Golf Classes
Golf Classes Holiday Camps
Holiday Camps  Rugby Classes
Rugby Classes Tennis Classes
Tennis Classes